Maintenance and care
The turbocharger is designed to last for the service life of the engine. The required monitoring is restricted to few periodic checks that should be made during every engine service. One condition for achieving longevity, however, is exact compliance with the engine manufacturer's servicing specifications - e.g. oil change intervals, oil-filter system maintenance, oil-pressure checks, cleaning all filter systems, and regular, professional filter changes. What is especially important when maintenance work is conducted on the air filter system: No foreign particles may enter the turbocharger.
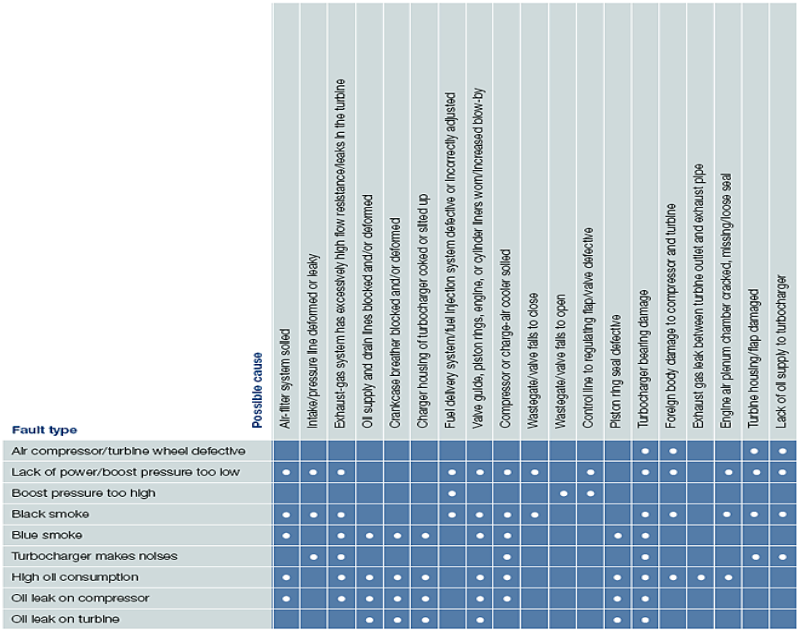
Power losses and faults - the causes are frequently not inside of the turbocharger
Power losses and faults in the engine are frequently caused by a defective turbocharger although it is still completely functional. To carry out rapid fault diagnostics, we have produced the table below to provide an overview of the possible causes.
How turbocharger damage is caused
Defects on the exhaust-gas turbocharger mostly have one of the following causes:
- Inadequate lubrication
If there is insufficient lubrication, the bearings will fail and the compressor and turbine wheels grind against their housings. - Dirty oil
Dirty lube oil leads to score marks on shaft journals and bearings. Oil bore holes and seals become clogged and cause high oil losses. - Intrusion of foreign bodies
Foreign bodies that, for example, enter through a defective air filter, damage the turbine or compressor wheels. The resulting unbalance damages the turbocharger bearing.